Scenario based SQL interview question how to extract domain from an email

In today's data-driven world, SQL proficiency is no longer a niche skill, it's a fundamental requirement for a vast array of roles, from data analysts and scientists to software engineers and database administrators. Consequently, SQL interview questions have become a cornerstone of the technical assessment process, often serving as a critical gatekeeper to your dream job.
Ever walked out of a SQL interview feeling like you could have done better? his article aims to demystify the SQL interview process by breaking down common question patterns and providing clear, concise, and effective solutions. We'll explore not just what to answer, but how to think through the problems, helping you build the confidence to articulate your SQL knowledge under pressure.
If you preparing for a SQL interview you can follow scenario based interview questions and answers to be interview ready.
1. How to extract only domain name from a email id field in Customer table.
In this article you will learn Scenario based SQL interview questions trending in 2025, so one of the trending question is How to extract domain name from an email with example of various Databases. Below is the customer table with customer id and respective customer data such as first name, last name, email ids of customer.
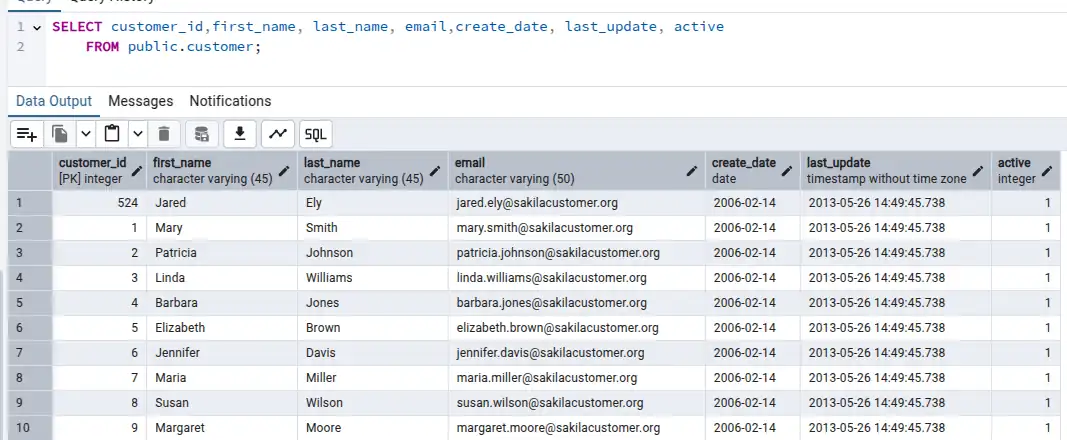
Above, we can see a field with "email" , lets observe the customer with customer id as '1' is having email id ad 'mary.smith@sakilacustomer.org' so here we have to extract only domain name which is 'sakilacustomer.org' in a separate field.
So how to achieve this lets see.
To Achieve this in SQL SERVER Database below is the SQL query:
SQL SERVER , supports CHARINDEX() Function in SQL Server for to find the position of a particular string inside a string.
SELECT SUBSTRING (email, CHARINDEX( '@', email) + 1,LEN(email))
AS domain_name from public.customer;
In general, the SUBSTRING Function allows three parameters, and they are Source, start point, endpoint.
- SUBSTRING function (or SUBSTR in some databases) is used to extract a portion of a string based on a starting position and length.
SYNTAX:
SUBSTRING(string_field, start_position, length)
string_field: This is the original string from which you want to extract a part. It can be a literal string or column name from a table ex (email id).
start_position: This is an integer that specifies where the sub-string should begin. In SQL, string positions are typically 1-indexed, meaning the first character is at position 1.
length: This is an integer that specifies how many characters you want to extract from the start_position. This parameter is often optional in some SQL dialects; if omitted, the function extracts all characters from the start_position to the end of the string.
Now we will see the start_position of sub-string where, CHARINDEX is being used to derive the start position of domain name where we calculate the start of domain name after the string value '@' only because the domain name will always be specified after the '@' symbol. So the task here was to find the position of string '@' in the email of a person and plus one to the position will be the start position of domain name.
Below is the syntax for CHARINDEX how it is being used.
SYNTAX:
CHARINDEX(substring, string_expression , start_location)
Example
SELECT CHARINDEX('is', 'This is techtutor');
-- Output: 3
The parameters of "CHAR INDEX"are defined below:
substring: Searching string field.
string_expression: This is the string inside which you are searching for the substring.
start_location (optional): This is an integer that specifies the character position to start the search. If omitted, the search begins at the beginning of string_expression (position 1).
Return Value:
CHARINDEX() returns an int representing the 1-based starting position of the sub string within the string_expression.
If the sub string is not found, it returns 0.
If any of the arguments are NULL, it returns NULL.
To Achieve this in PostgreSQL Database below is the SQL query:
To achieve the same in PostgreSQL the syntax will be little difference instead of CHARINDEX it supports function called POSITION the output will be the same.
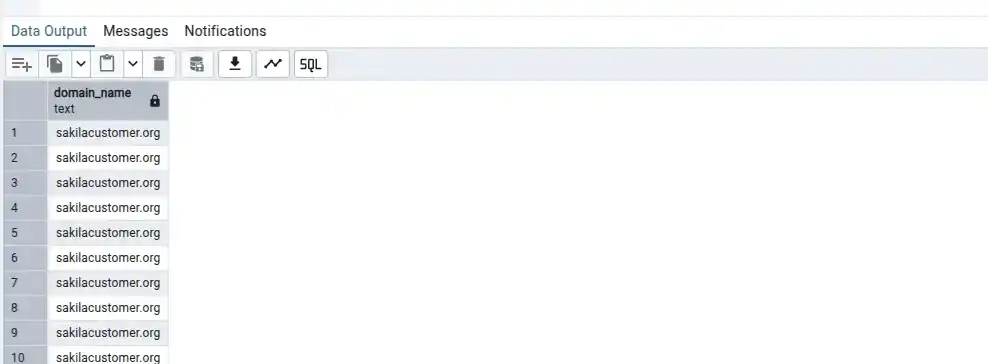
select substring(email, position('@' IN email)+1, length(email))
as domain_name from public.customer;

POSITION(): function is used in PostgreSQL DB to find the starting position of a specified sub-string within a larger string using that search string it will give the position of the field as in this case our searching string is '@' so it will provide position of this string in every email plus 1 will count from next position to find the domain name.
SYNTAX:
POSITION(substring IN string)
To Achieve this in ORACLE/MYSQL Database below is the SQL query:
To achieve the same in oracle/MYSQL the syntax will be little difference as the POSITION() function is only for POSTGRESQL in oracle/MYSQL DB we have instring() or instr() function for same results. It's a very powerful and versatile function for text manipulation.
select substring(email, instring('email','@')+1, length(email))
as domain_name from public.customer;
SYNTAX:
INSTR(string, substring)
Example
SELECT INSTR('This is Techtutor', 'T') FROM DUAL;
-- Output: 9
string: The main string in which you want to search.
substring: The string you are looking for.
