10 Most commonly used Unix commands
In this article we will learn some most basic UNIX commands, If you are a fresher or new to Unix this article will help you learn and understand the most basic Unix commands which any one can learn in few minutes. Also, these are frequently asked questions in interview.
Lets move to the point why UNIX commands are required, so the answer is to interact with Unix operating system Unix commands are required to interact through terminal to manage and perform the task like manage the files, execution of programs in UNIX OS and controlling the processes.
1. How to list files in UNIX:
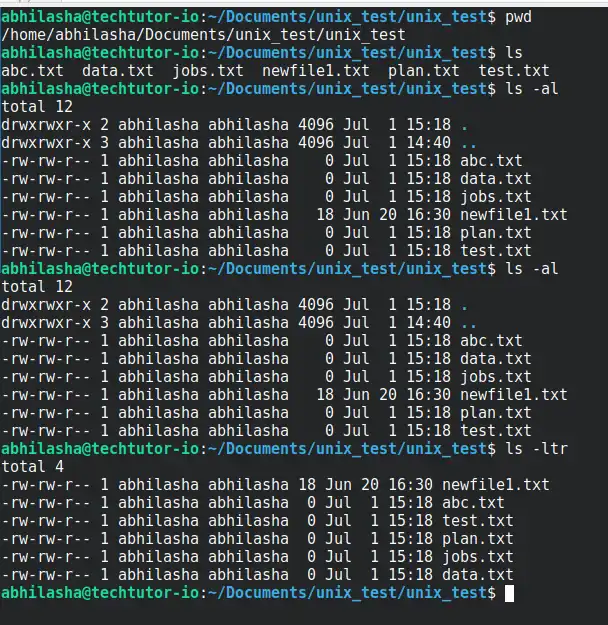
ls is used to list files in current directory in Unix.
ls commands can be used with options such as '-l,-a,-r,-al,'
Syntax: ls [options] [directory_or_path]
- ls -l: Long format listing (permissions, owner, size, date, etc.).
ls -l
- ls -a: Lists all files, including hidden files (those starting with a dot).
ls -al
- ls -lt: to list which files were recently changed or updated
- ls -r: To list items inside sub folders, add the -R option
ls -ltr
2. How to navigate through directories:
cd command is used to Change Directory. Moves you to a different directory.
Syntax:
cd [path_or_directory]
cd /home/Documents/folder/
- cd ..: Move up one level in the directory tree.
- cd ~: Go to your home directory.
- cd -: Go to the previous directory you were in.
3. How to create a directory in Unix:
mkdir: To Creates a new directory in Unix mkdir command is used.
Syntax:
mkdir [directory_name] ---new directory name
mkdir folder1
4. How to remove/delete file/ directory in Unix:
rm command is used to remove/delete files from a folder . rm can be used with different [options] based on file or directory actions.
- rm -r [directory]: Recursively deletes directories and their contents (use with extreme caution!).
rm -r
- rm -f [file]: Force deletion (overrides write protection, use with caution!).
rm -f
- rmdir [directory_name]: Removes a directory. Deletes an empty directory.
rmdir
5. How to create a file in unix:
touch Creates an empty file or updates the timestamp of an existing file with .txt/.csv file extension.
Syntax:
touch mynew_file.txt ----creates a new empty file named "mynew_file.txt".
6. Using the echo/cat command with redirection to add content to the file at the time of creation:
This will add text while file creation.
echo "This is some text.">> mynew_file.txt
Cat can be used to view the content of file
cat > my_new_file.txt ---
7. How to copy file from one to another path in Unix:
cp command is used to Copy files or directories from one to other path.
Syntax:cp [source] [destination] --- Copies files or directories.
cp /home/folder1 /home/folder2
8. How to change File Permissions and Ownership in unix:
chmod is used to changes file permissions in unix.
Syntax: chmod [options] [permissions] [File_name]
chmod 777 file.txt
Above will give all read,write,execute permission.
understanding permission in file
- Read (r): Allows viewing the contents of a file or listing a directory's contents.
- Write (w): Allows modifying a file or creating/deleting files within a directory.
- Execute (x): Allows running a file (if it's an executable) or accessing a directory
9. chown [user][:group] [file]: Change owner. Changes the owner and/or group of a file or directory.
To give user access for the file who all can who have the Access?
- User (u): The owner of the file or directory.
- Group (g): Users who are members of the file or directory's group.
- Others (o): All other users on the system
10. How to check current working directory in unix:
pwd command is used to check the current working directory.
Syntax: below will give path of current working directory.
pwd
output: /home/folder/page1
Note: for more detail in Unix command you can check more articles on Unix.
